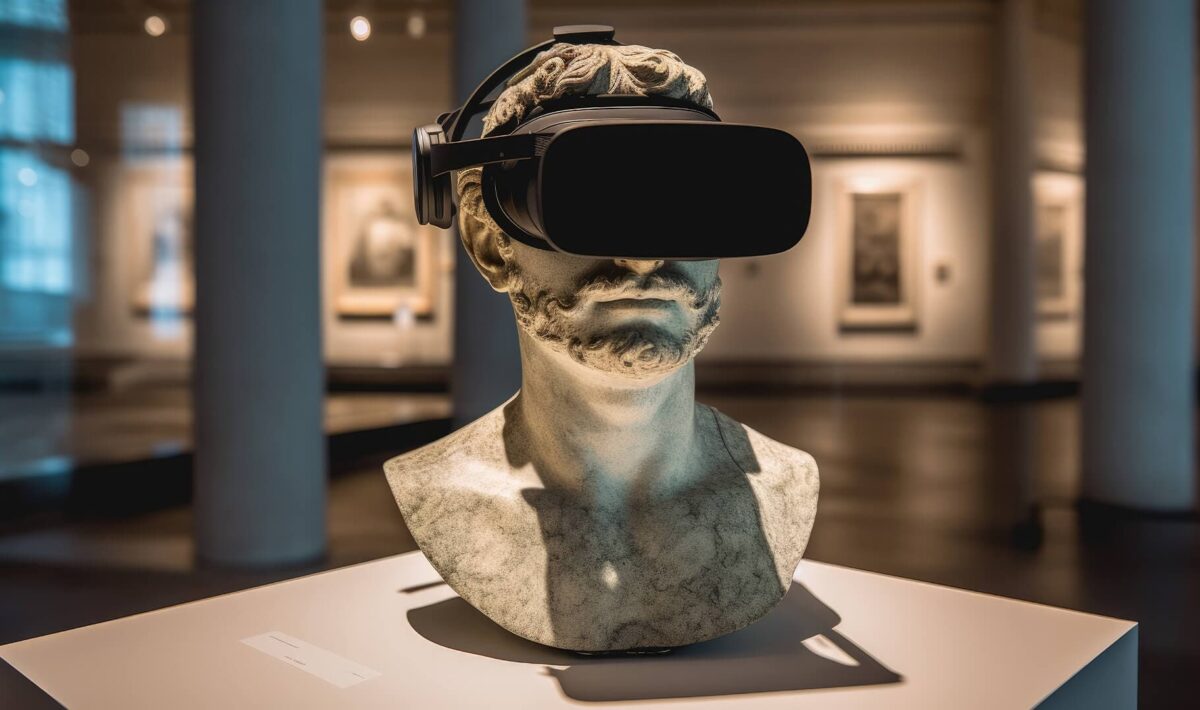
Digitization is rapidly permeating all areas of life, and culture is no exception. Today, we are witnessing not only the development of new forms of art but also a complete rethinking of how it is presented. Virtual museums, interactive exhibitions, and digital canvases have become part of everyday reality. This is not merely a replacement for traditional galleries but a true cultural shift that opens new horizons for both creators and viewers.
A New Face of Museums: Digital Transformation
Visiting a museum used to be associated with tickets, tour guides, and strict schedules. Today, all of that is accessible without leaving your home. Virtual museums are online spaces where exhibitions are presented in the format of 3D tours, augmented or virtual reality. Projects like Google Arts & Culture or the virtual Louvre gallery allow people to explore world heritage in exquisite detail. This is particularly important for residents of countries like the Czech Republic, where it’s not always possible to visit major international museums in person.
Interestingly, these technologies are also actively used in other areas of online entertainment. For example, when visiting a nové české online casino, one can notice that the interface is built on the same visual principles as digital galleries: intuitive navigation, visually rich environments, and a personalized experience. This parallel demonstrates how unified technological solutions are reshaping our perception of digital space — whether you are in a virtual room with Van Gogh’s paintings or choosing a slot game on a zahraniční online casino platform.
Digital Art as a Form of Self-Expression
With the rise of NFTs, AI-generated artworks, and interactive visual installations, traditional understandings of art have undergone significant changes. Digital art is not just PNG files or 3D objects. These are complete projects that engage the viewer in a process of interaction, turning them from a passive observer into an active participant. Such forms of art are especially popular among young people who have grown up in a state of constant online presence.
Today’s digital artists use not only Photoshop or Blender but also neural networks, code, and even game engines to create their works. Some projects are integrated into metaverses, where users can explore virtual spaces created by artists, participate in performances, and interact with the surrounding digital world in real time.
Democratizing Culture: Art Becomes More Accessible
One of the main advantages of virtual museums and digital art is accessibility. People from small towns in the Czech Republic or remote regions can now engage with global culture without needing to travel to Prague, Paris, or New York. A stable internet connection and a desire to explore are all that’s needed.
Moreover, the digital format breaks down traditional barriers: paid tickets, limited visiting hours, physical distance. This creates an entirely new approach to the distribution of cultural heritage. Museums are becoming more open, flexible, and adapted to a diverse audience — from schoolchildren to NFT collectors.
Challenges and Criticism
Despite the obvious advantages, the digitization of art raises many questions. First, the physical interaction with the object is lost. It is impossible to feel the texture of a painting, appreciate the scale of an installation, or immerse yourself in the atmosphere of an exhibition hall. Second, there are doubts about the authenticity of the experience: how deeply can one feel the “Mona Lisa” through a screen?
There’s also the issue of copyright and authenticity of digital objects. In a world where copying a file takes just a second, the question of “what is the original?” becomes increasingly relevant. This is especially true for NFTs, where the uniqueness of an object is confirmed by a blockchain record but is visually indistinguishable from a copy.
Looking Ahead: Culture in the Metaverse
With the development of Web3 and VR technologies, culture is becoming part of a global digital space. Virtual auctions, exhibitions, and art festivals are already being held, with participants from all over the world. Some museums are beginning to create their own tokens or exhibitions in metaverses, where anyone can “visit” the display using an avatar.
For the Czech audience, this can become an especially important tool for preserving national heritage and showcasing it abroad. Virtual Czech museums can already be embedded into international platforms and reach thousands of viewers worldwide — regardless of their geographical location or language barriers.
Conclusion
The future of culture is undoubtedly tied to digital technologies. Virtual museums and digital art are not a temporary phenomenon but part of a new cultural paradigm. They make art more accessible, interactive, and flexible. And while physical museums will continue to be an important part of cultural infrastructure for a long time, it is the digital environment that will shape how we perceive art in the 21st century.
It’s entirely possible that in the coming years, visiting a virtual museum will become as common as playing at a zahraniční online casino or taking part in digital exhibitions within the metaverse. Culture is becoming closer — all you have to do is reach out to the screen.